Introduction: Making SharePoint Relational
SharePoint is great, but it's not inherently relational. That’s where the Associated Items column of Infowise Ultimate Forms fills the gap. Designed to turn SharePoint lists into application-style data structures, it lets you:
-
Create related items (tasks, line entries, documents) right from the parent item
-
View and manage them directly from parent forms or list views
-
Add repeating sections and embed detailed, structured data (like RFPs or invoices)
This rich, relational capability transforms SharePoint into a true business platform.
Linking Parent and Child Lists: Two Methods Explained
When using Associated Items you can establish the relationship in two ways:
-
Standard Lookup Column
-
Add a lookup column in your child list pointing to the parent.
-
This approach is straightforward for basic relational setups and auto-fills the link.
-
-
Associated Content Types
-
Infowise provides hidden relationship columns behind the scenes.
-
This enables multiple associated columns in the same list (e.g., corrective vs. preventive actions).
-
This flexibility streamlines building robust, relational structures in SharePoint without manual overrides.
Flexible Data Entry Options
Associated Items column is highly configurable, allowing you to enter data just the way you need it.
- Pop-up form - add or update items using a pop-up form. Best for complex child forms with advanced logic.
- Grid entry - add or update child items directly inside a grid within the parent form. Only the columns included in the grid view are visible and updateable. This is perfect for simple solutions, such as Expense Reports.
- Embedded form - each item is displayed as a form right within the parent form. Combines form-level logic requirements with streamlined unified interface. Perfect for smaller forms that still require specific layout or logic.
Deep Integration within Ultimate Forms
Associated Items columns are not just limited to forms. Other components within Ultimate Forms can display and manage associated items seamlessly, making it easy to create advanced business solutions without any code.
- Print - include associated items in print-outs, PDFs, Word documents, etc. With Associated Documents, you can embed document content in the generated PDFs.
- Alerts - include associated items in the body of the email alerts and provide all the necessary information to the recipients, even outside of your organization.
- Actions - generate and link associated items and documents in your workflows.
- List Search and Rollups - access associated items directly from parent views
As with all our features, we invest a great deal of effort into simple, but sophisticated lateral integrations.
Summary Columns: Automate Calculations on Child Items
Once relational links are established, Associated Items Summary columns elevate your data with real-time insights such as:
-
Count — e.g., number of invoice line entries or active tasks
-
Sum / Average / Standard Deviation - useful for calculations like invoice totals or average support resolution times
-
Concatenate text - e.g., combining child item comments into one parent field
- Minimum / Maximum - available for both numbers and dates
The feature updates automatically whenever child items are added, edited, or deleted. The results are stored on the parent item and reflected in real time, even when child items are updated externally (outside the parent form).
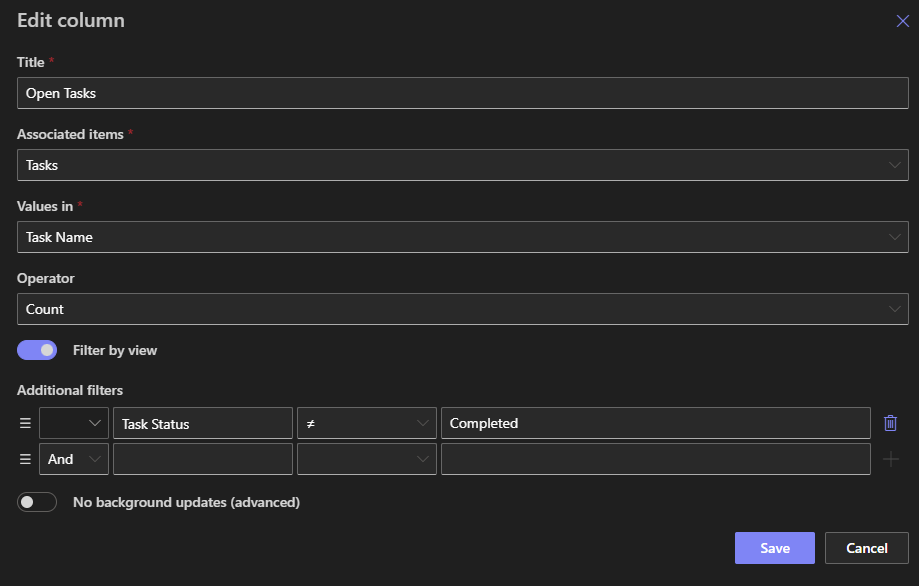
Setup Guide: Creating a Summary Column
To configure Associated Items Summary:
-
Ensure the Associated Items column already exists in the parent list.
-
Add a new Associated Items Summary column.
-
Configure its settings:
-
Target Associated Items column (the parent-child relationship)
-
Column to Calculate (e.g.,
Amount,Score) -
Operation Type (Sum, Count, Avg, etc.; only Count or Concatenate if the target isn't numeric)
-
Optionally, apply conditions to focus summaries on specific child items - like only counting tasks where Status ≠ Completed. Use validation rules on the parent form to prevent saves when related data doesn’t meet criteria, such as allowing closure only when no open subtasks remain.
Real-World Scenarios: How Businesses Use It
1. Invoice Management
Auto-calculate total invoice amount from line items (Sum) and track the number of items (Count). Prevent finalizing an invoice if child lines are missing or flagged with errors.
2. Project Task Tracking
Display open tasks (by adding a condition based on Status), compute average time to close, and block project closure until all tasks are completed.
3. Support Centers
Aggregate average resolution time or compute total escalated cases per ticket category, improving support SLA insights.
4. Sales Reporting
Monitor total sales amount per customer or average order value, updating live as orders are logged.
5. Inventory Management
Track stock value automatically by summing quantities times cost, helping avoid manual errors and stale data.
6. Employee Training
Record total training hours and count of sessions per employee - helpful for compliance and workforce planning.
7. Marketing Campaigns
Show number of campaigns launched and average return rate, while concatenating campaign outcomes for quick review.
Validation & Business Logic Built In
These summary values aren’t just static, they can be integrated into business logic:
-
Form Validation: Block saving a parent item until essential child items exist or minimum values are met.
-
Conditional Behavior: Show banners or warnings in forms when summaries fall outside expected thresholds.
-
Workflow Triggers: Launch automated actions when calculated summaries cross thresholds (e.g., order overspending).
Best Practices for Effective Use
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Conditions Smartly | Focus summaries on relevant child records to improve clarity (e.g., open only, or date-based subsets). |
| Optimize Performance | Only apply summaries where necessary, especially in large datasets. Leverage indexing where possible. |
| Combine with Views & Grouping | Group parent list by conditions like high totals or overdue subtasks for quick oversight. |
| Use for Dashboards | Create dashboards summarizing totals, averages, or counts across parent items. |
| Simplify UX with Tabs | Display summary columns alongside associated sections via forms for easy review and interaction. |
Enhanced User Experience: Tabs & Real-Time Updates
To make summaries more engaging:
-
Use Forms Tabs (via Ultimate Forms) to arrange columns and child grids tidily (e.g., show
Setup Cost,Execution Cost,Completion Coston subforms). -
The summary values refresh instantly, even when child items are modified outside the parent form, delivering a fluid, real-time experience.
Advanced Use: Calculated Actions & Conditional Flows
Explore the Infowise Calculate Summary action to expand dynamic logic beyond associated items:
-
Use conditions to sum or count values across lists and update current item fields or raise errors.
-
Example: Prevent booking when the total scheduled hours exceed a quota.
This action can also evaluate conditions (All / Any), enabling error-based logic for compliance or gatekeeping.
Summary: What This Feature Enables
-
Relational Empowerment: Transform flat SharePoint into dynamic, relational lists.
-
Calculative Intelligence: Live summaries like counts, sums, and averages enrich data visibility.
-
Business Logic Integration: Trigger workflows, validations, and UI cues based on summaries.
-
Automation & Scalability: Aggregate, filter, and monitor without scripts across lists and libraries.
-
Enhanced UX: Display meaningful data in real-time through forms, tabs, and dashboards.
Wrapping Up
The Associated Items and Summary columns in Infowise Ultimate Forms powerfully augment SharePoint’s capabilities, making it relational, dynamic, and business-ready. From financial tracking to campaign insights, real-time summaries bring clarity, accuracy, and automation without custom code.
Whether you're preventing incomplete data saves, building dashboards, or enforcing business rules, these tools scale with your process needs and work behind the scenes to maintain data integrity.
